Introduction
About 40%–50% of infertility cases are due to male factors, which may involve one or a combination of the following:
Asthenospermia (poor sperm motility)
Oligospermia (low sperm concentration)
Teratospermia (abnormal morphology)
Collectively defined as oligo-astheno-teratospermia
Study details
A meta-analysis was conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines.
Total studies analysed:
Six randomised clinical trials conducted between 2012 and 2022.
Treatment and duration:
Various doses of Myo-inositol administered for durations ranging from 30 minutes to 6 months.
Results
There were a significant improvements in several sperm parameters following Myo-inositol therapy:
- Total sperm motility
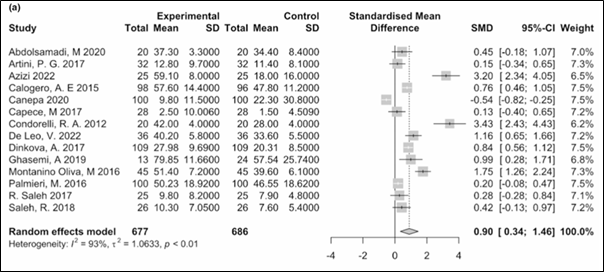
Significant increase (SMD 0.90; 95% CI: 0.34–1.46; p = 0.001) (Figure 1)
Figure 1. Results of the meta-analysis for total sperm motility.
SD: Standard difference; SMD: Standardised mean difference; CI: Confidence intervals.
- Progressive sperm motility
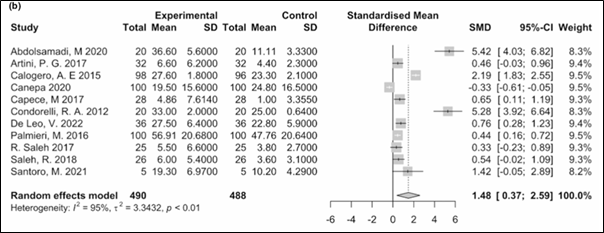
Significant increase (SMD 1.48; 95% CI: 0.37–2.59; p = 0.008)
(Figure 2)
Figure 2. Results of the meta-analysis for progressive sperm motility.
SD: Standard difference; SMD: Standardised mean difference; CI: Confidence intervals.
- Testosterone levels
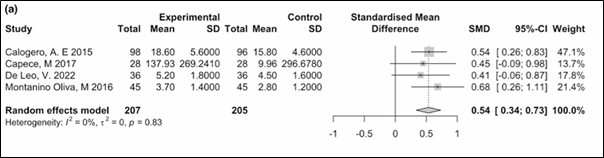
Significant improvement (SMD 0.54; 95% CI: 0.34–0.73; p < 0.0001)
(Figure 3)
Figure 3. Results of the meta-analysis for testosterone levels.
SD: Standard difference; SMD: Standardised mean difference; CI: Confidence intervals.
- DNA fragmentation
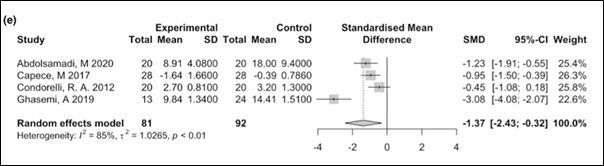
Significant decrease (SMD −1.37; 95% CI: −2.43 to −0.32; p = 0.01)
(Figure 4)
Figure 4. Results of the meta-analysis for spermatozoa with DNA fragmentation.
SD: Standard difference; SMD: Standardised mean difference; CI: Confidence intervals.
Conclusion
Myo-inositol therapy improves total and progressive sperm motility and testosterone levels, with a reduction in sperm DNA fragmentation, indicating its potential as a safe and effective option for the management of infertility in males.
Abbreviations
CI: Confidence intervals; IVF: In vitro fertilisation; PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; SMD: Standardised mean difference